Table of Contents
If you’re curious about the fascinating celestial entities defining our solar system, you’re in the right place for your cosmic exploration. We’ll journey to unveil a brief overview of what is in our solar system, beginning with our radiant sun to the distant edges of our celestial neighborhood.
But first, we need to understand…
Why is Understanding What is in Our Solar System Crucial?
Understanding what’s in our solar system isn’t just about looking at stars; it’s about figuring out the stuff that makes us exist. This journey explores how planets and other things in space move together. It’s not just interesting—it’s finding out the secrets that tie these space neighbors. Let’s sail through space, figuring out what makes up our solar system and the cool stories they hide. The big deal here is getting why these space things matter, revealing tales that made our world.
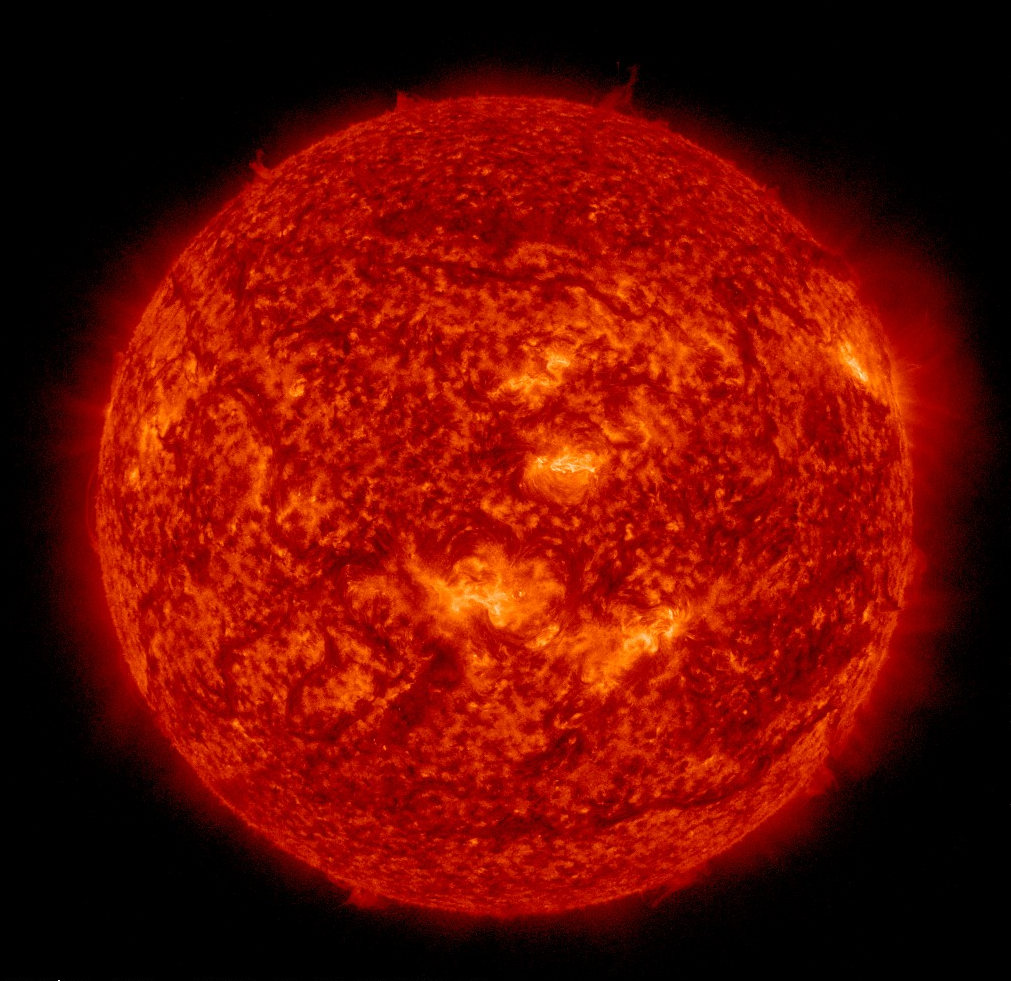
The Sun
What is in our solar system that shapes its very essence? It’s the sun, the heartbeat that fuels the dance of our solar system. It’s so big that its gravity keeps all the planets, including Earth, moving around it. This makes the sun the boss, directing the planets in their paths and making sure everything stays in order. Besides being a bright light in the sky, the sun has cool features like sunspots and solar flares, showing that it has a kind of magnetic power that affects everything in our solar system. Learn how to safely observe the sun with a telescope here.
Facts About the Sun:
- The sun is mostly made of hydrogen and helium.
- It's really, really hot on the surface, more than 5,500 degrees Celsius (9,932 degrees Fahrenheit).
- Solar flares are powerful bursts of energy that the sun sometimes shoots out.
- Sunspots are cooler spots on the sun's surface, and they come and go in cycles.
- The sun makes energy through a process called nuclear fusion in its core
Inner Planets
As we continue to explore what is in our solar system, we shift our focus to the inner planets – Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars. These terrestrial worlds, closer to the sun, have stories to tell and mysteries to unfold.
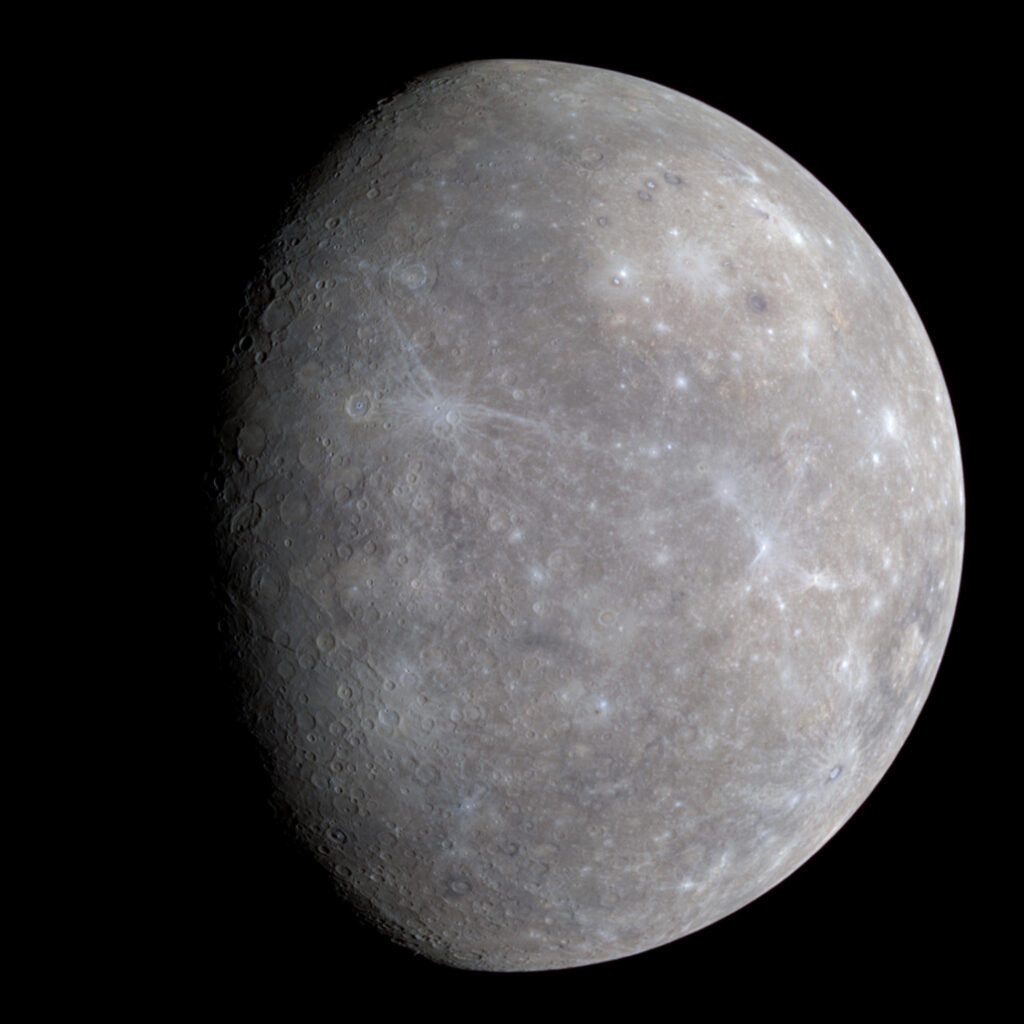
Mercury
Mercury, known as the swift messenger of the gods, is the planet closest to the sun. With its scorching surface and no atmosphere, it’s a world of extremes. Studying Mercury is like figuring out a piece of the cosmic puzzle, helping us understand how our solar system works.
Facts about Mercury:
- Mercury has extreme temperature variations, with daytime temperatures soaring as high as 800 degrees Fahrenheit (427 degrees Celsius) and nighttime temperatures dropping drastically.
- Unlike Earth, Mercury has a thin and virtually nonexistent atmosphere. This lack of atmosphere means there's nothing to trap heat, resulting in dramatic temperature fluctuations.
- Mercury has a slow rotation on its axis but a swift orbit around the sun. It completes three rotations for every two orbits around the sun, which means a day on Mercury (one full rotation) takes about 59 Earth days.

Venus
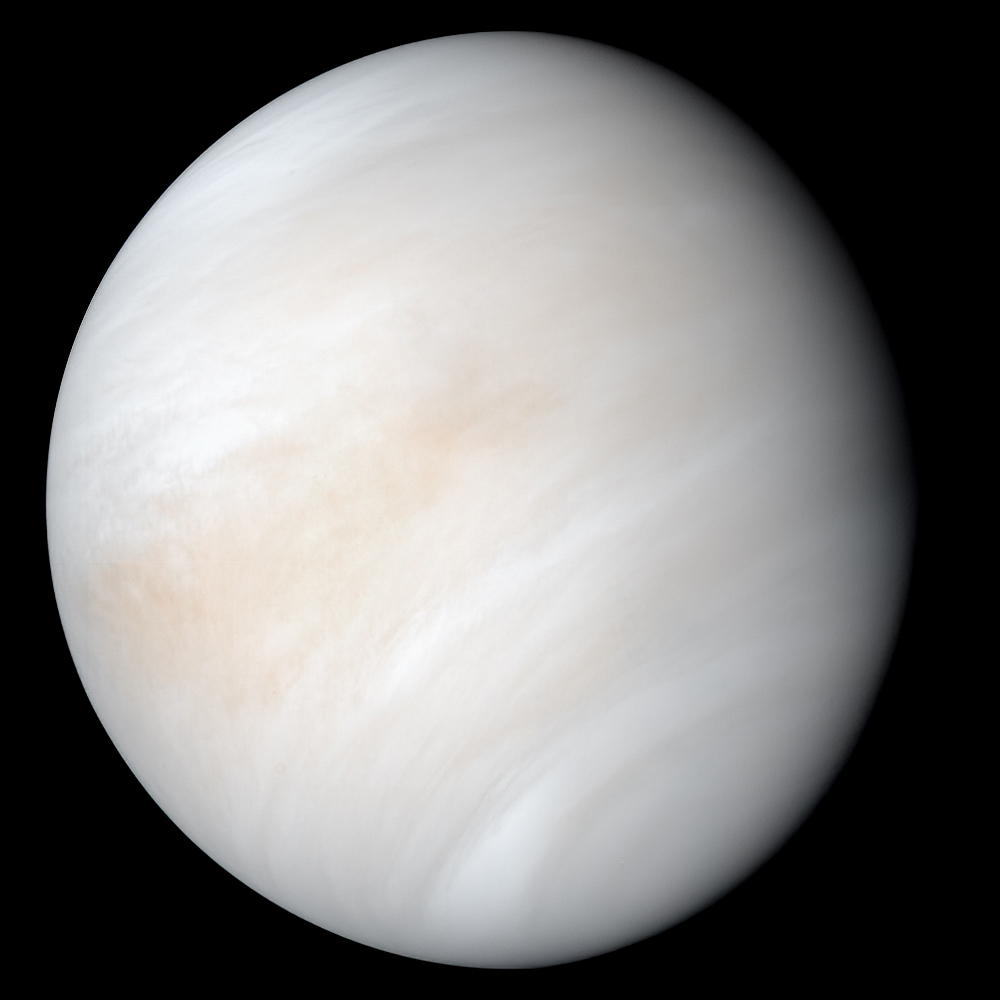
Moving outward, we encounter the enigmatic beauty of Venus. Veiled in thick clouds, this planet has a greenhouse effect that turns its surface into a scorching hot environment. Yet, beneath the clouds lies a world with geological wonders waiting to be discovered.
Facts about Venus:
- Venus rotates in the opposite direction to most planets, causing the sun to rise in the west and set in the east.
- Venus has a thick, toxic atmosphere, mainly composed of sulfuric acid, creating extreme pressure and temperatures at its surface.
- Venus boasts vast volcanic plains and thousands of volcanoes, suggesting periodic resurfacing.

Earth
Earth, our home, is a crucial player in the solar system. Beyond being a familiar place, it holds the key to life. Earth’s intricate systems, from the oceans to the atmosphere, shape the very fabric of our existence. In our exploration of “what is in our solar system,” Earth becomes both a point of interest and a valuable reference, providing insights into the conditions necessary for life and the workings of planetary systems.
Facts about Earth:
- Earth's atmosphere is composed mainly of nitrogen and oxygen, creating a breathable environment for life. It protects us from harmful solar radiation and regulates the planet's temperature.
- Earth has a magnetic field generated by its iron-nickel core. This shield helps protect the atmosphere from solar winds and cosmic radiation.
- Earth's oceans contain not only the majority of the planet's water but also diverse ecosystems and the longest mountain range, the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, hidden beneath the waves.
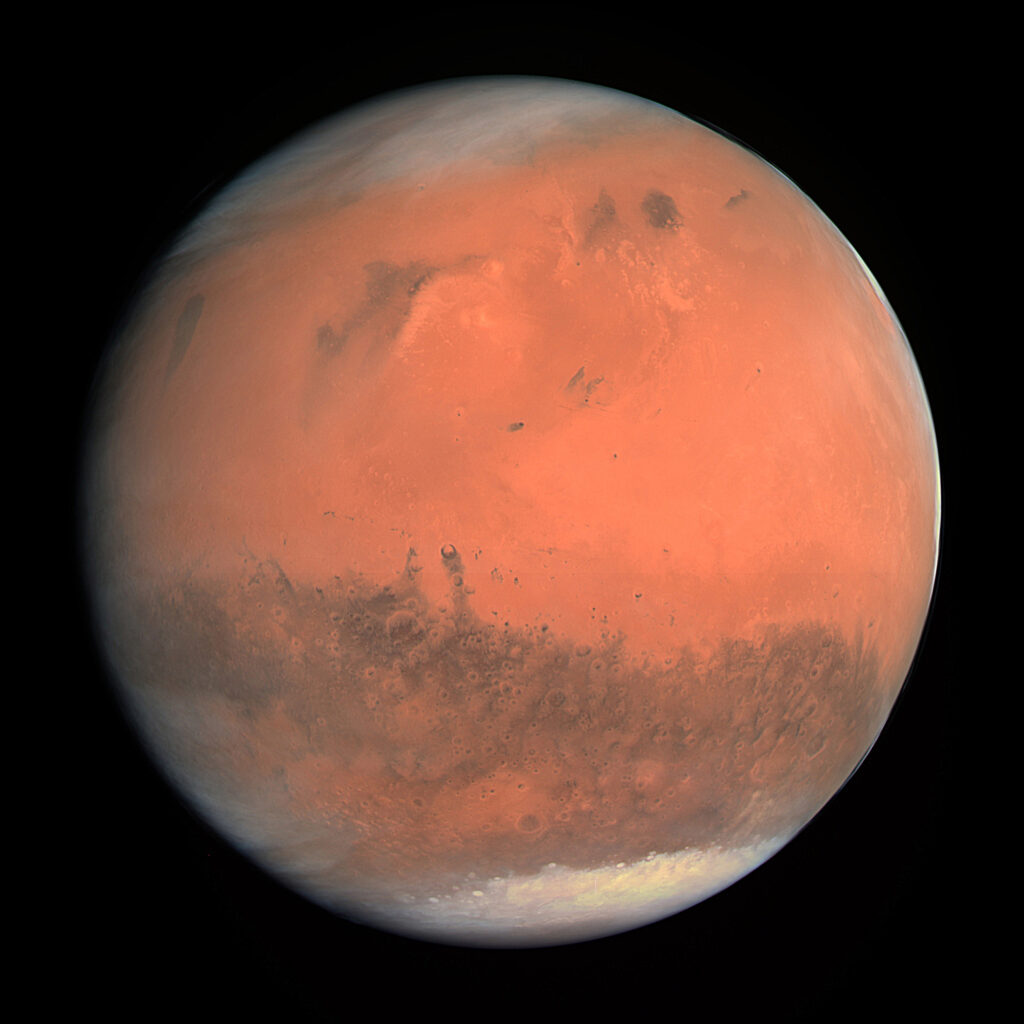
Mars
And then, there’s Mars, often referred to as the Red Planet. Known for its rusty surface and a rich history of exploration missions, Mars continues to captivate our imagination. Unraveling the mysteries of Mars goes beyond its distinct appearance; it’s about exploring the potential for life beyond Earth.
Facts about Mars:
- Mars hosts the largest volcano in the solar system, Olympus Mons, towering over 13 miles (21 kilometers) high.
- Mars has a thin atmosphere, mostly composed of carbon dioxide, creating a surface pressure less than 1% of Earth's.
- Although Mars is currently arid, evidence suggests the presence of liquid water in its past, raising questions about the planet's potential habitability.

Asteroid Belt
Our exploration of “what is in our solar system” takes us to the asteroid belt, a vast region positioned between Mars and Jupiter. Composed of rocky remnants, the asteroid belt originated from protoplanetary material that never coalesced into a full-fledged planet, providing crucial insights into the early solar system.
Within the asteroid belt, the gravitational pull of Jupiter has played a crucial role in shaping its composition. Jupiter’s immense gravity prevented the accumulation of material within the belt, inhibiting the formation of a larger planet. This planetary influence has led to a diverse array of sizes among the asteroids. While some are mere rocky fragments, others, like the dwarf planet Ceres, achieve substantial size.
Adding to the belt’s complexity are certain asteroids that exhibit distinctive geological features. Notable among them is Vesta, showcasing intriguing surface characteristics. These variations contribute to the rich tapestry of the asteroid belt, providing valuable insights into the diverse nature of these celestial remnants.
While the asteroids in the belt are not commonly considered an imminent threat to Earth, collisions and impacts between celestial bodies in the solar system have occurred in the past and will continue to do so over time.

Outer Planets
Beyond the asteroid belt, our investigation into what is in our solar system brings us to the gas giants – Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. These immense planets, characterized by their predominantly gaseous composition, introduce a new facet to our exploration.
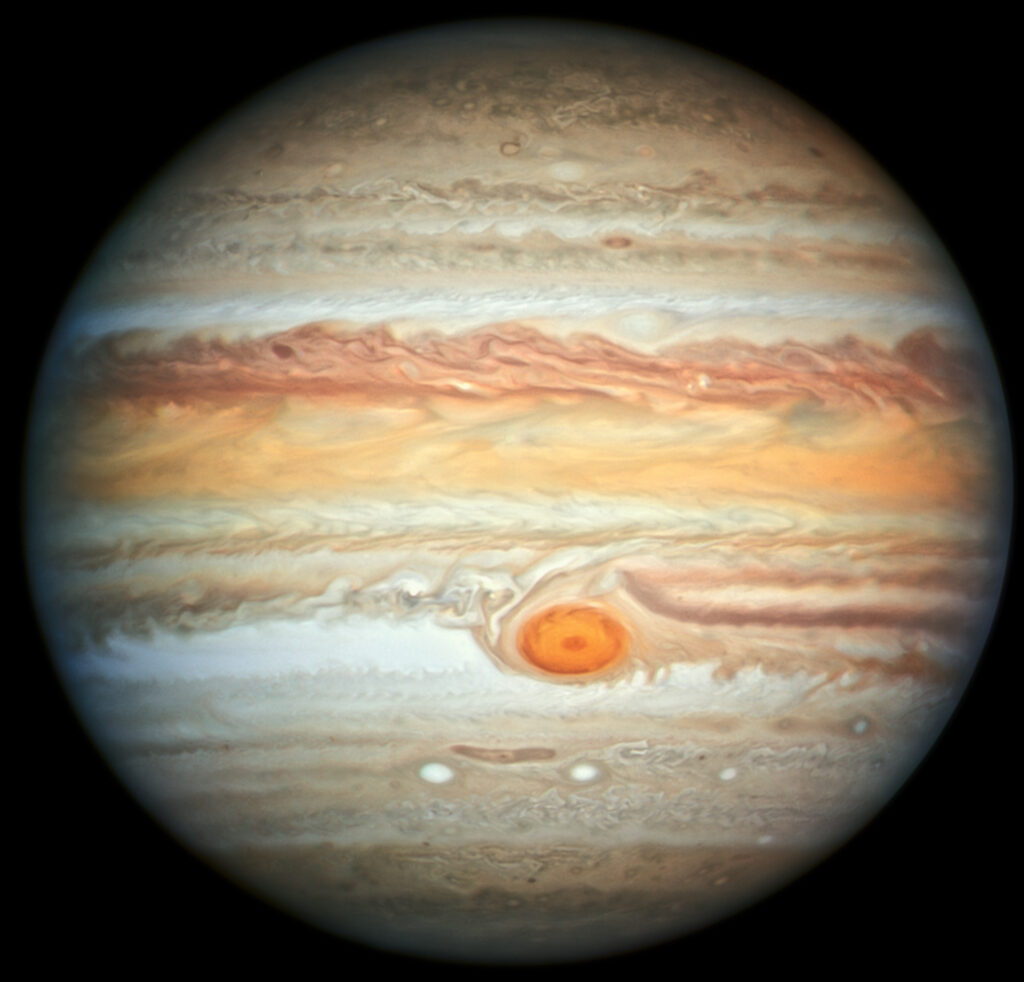
Jupiter
Jupiter, the largest of them all, dominates the outer reaches with its immense size and powerful storms. As we marvel at its iconic Great Red Spot, we witness the grandeur of this gas giant. Jupiter’s entourage of moons, each a unique world in its own right, enriches our understanding of the outer planets.
Facts about Jupiter:
- Jupiter, the gas giant in our solar system, is so massive that it could contain more than 1,300 Earths within its voluminous form, earning its distinction as the largest planet.
- Jupiter's colossal size contributes to its powerful magnetic field, the strongest among all the planets in our solar system. This intense magnetic field creates a protective magnetosphere, shielding Jupiter and its moons from solar winds and cosmic particles
- Jupiter has a faint ring system, primarily composed of dust particles and small rocks, thought to be material ejected from its moons through processes like micrometeoroid impacts.

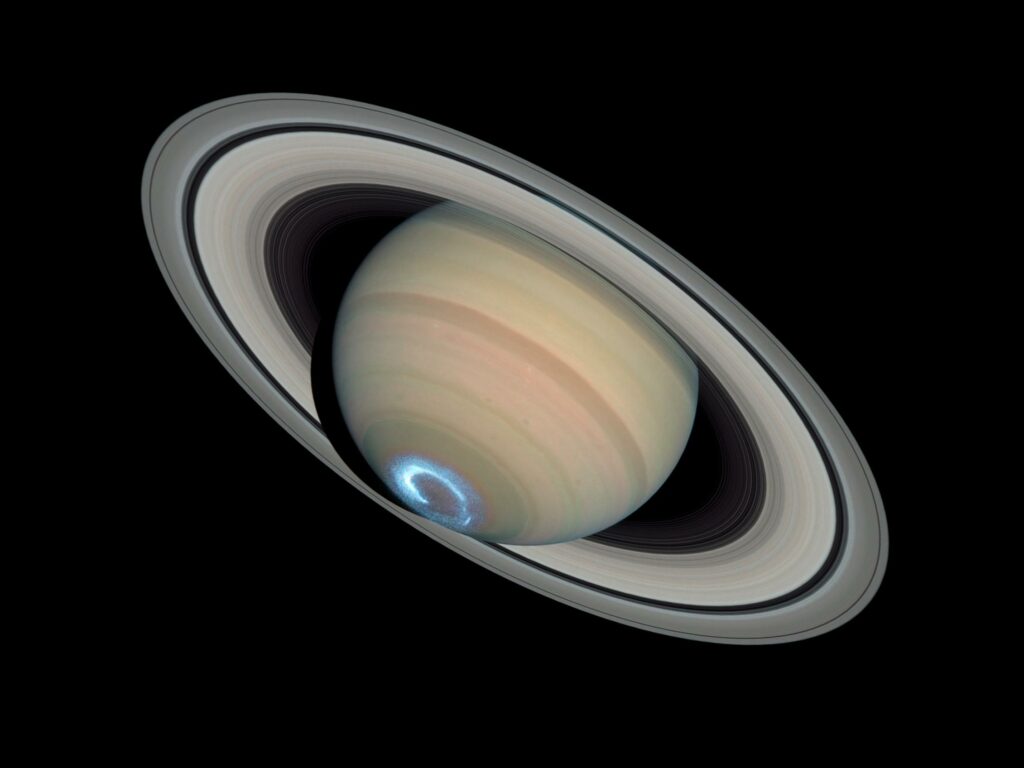
Saturn
Continuing our journey outward, we come across Saturn, distinguished by its captivating ring system. Composed of numerous icy particles, Saturn’s rings intrigue scientists, prompting exploration into the mysteries surrounding their formation.
Facts about Saturn:
- Saturn's iconic ring system, a dazzling display of icy particles and debris, spans an impressive 280,000 kilometers in diameter and is divided into numerous distinct bands, each with its own unique characteristics.
- Saturn is one of the fastest-spinning planets in our solar system, completing a rotation on its axis in approximately 10.7 hours.
- Saturn, a gas giant akin to Jupiter, predominantly consists of hydrogen and helium. Its gaseous atmosphere showcases intricate features, including cloud bands, storms, and the famous hexagonal storm pattern observed at its north pole, adding to the distinct allure of this majestic planet in our solar system.
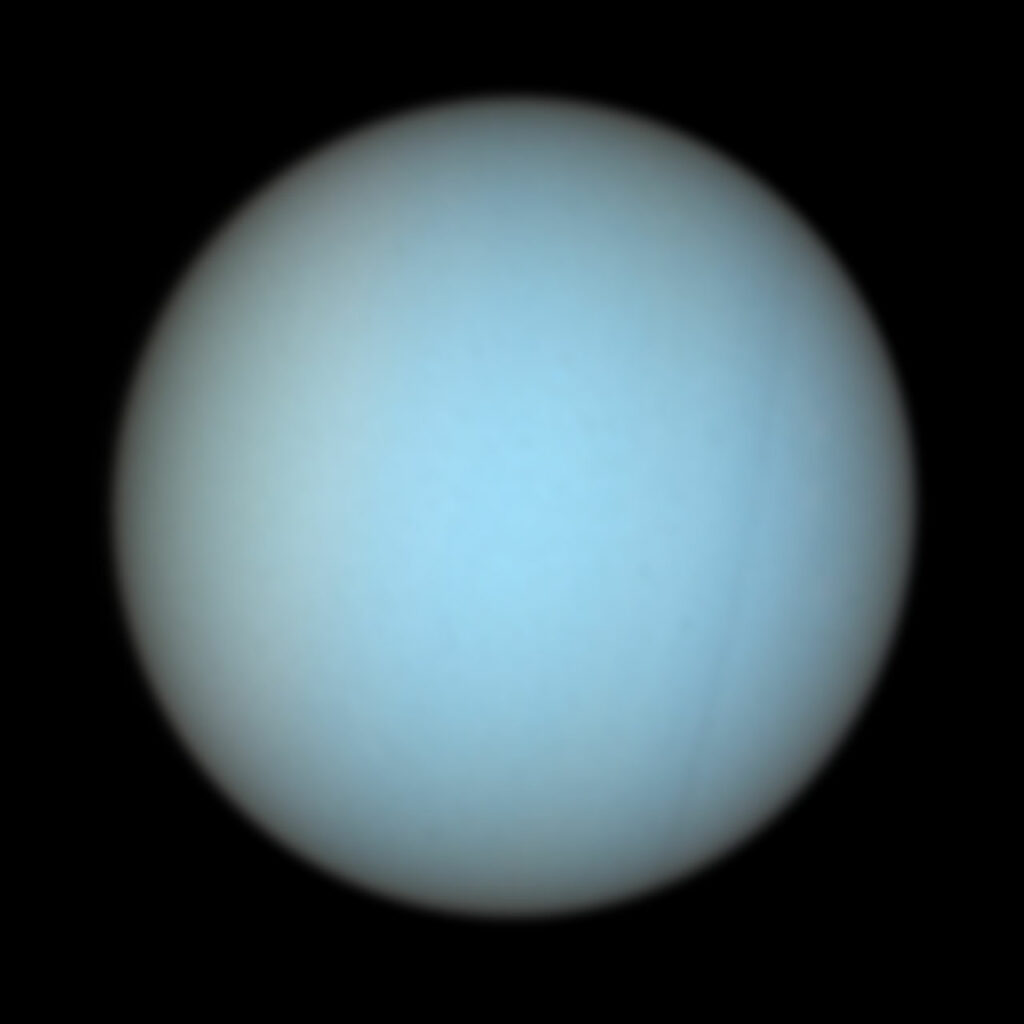
Uranus
Uranus, distinguished by its peculiar tilt, prompts an exploration of its distinctive features. With its rotational axis tilted at an extreme angle, Uranus challenges conventional understandings of planetary dynamics.
Facts about Uranus:
- Uranus boasts an unusual retrograde rotation, spinning opposite to the majority of other planets in our solar system, contributing to its distinctive character.
- Uranus has a highly tilted magnetic field, deviating significantly from its rotational axis. This peculiarity sets it apart from the magnetic fields of other planets.
- Uranus features a frigid atmosphere primarily composed of hydrogen, helium, and methane. Its icy, serene appearance is a result of the methane in its upper atmosphere, giving the planet a distinctive blue hue.

Neptune
Concluding our exploration of the gas giants, Neptune, situated at the outermost reaches, marks the end of our journey. Enveloped in deep blue storms, Neptune’s windswept atmosphere presents a captivating spectacle. In the study of the outer planets, the interplay between these gas giants and their moons contributes to our understanding of the solar system’s dynamics, providing valuable insights into what is in our solar system.
Facts about Neptune:
- Neptune's distinct deep blue color comes from the presence of methane in its atmosphere, absorbing red light and reflecting blue hues.
- Neptune boasts the fastest winds in our solar system, reaching speeds of over 1,200 miles per hour. Its dynamic atmosphere features large storms, including the famous Great Dark Spot.
- Neptune has a pair of remarkably similar moons, Naiad and Thalassa, which are both irregularly shaped and roughly 60 kilometers in diameter. Their close proximity and shared characteristics make them a unique duo among the solar system's moons.
The outer planets, with their immense size and intricate systems, beckon us to peer into the cosmic tapestry of our solar system. As we continue our celestial odyssey, let’s unravel the mysteries of these distant giants and appreciate the vastness that extends far beyond the familiar orbits of the inner planets.
Dwarf Planets and Kuiper Belt
Exploring the outer edges of our solar system, we encounter dwarf planets and the Kuiper Belt. Dwarf planets, smaller planetary bodies, inhabit this region along with the Kuiper Belt, a zone beyond Neptune filled with numerous icy bodies. This journey provides insights into the composition and dynamics of what is in our solar system.
Pluto
Pluto, once labeled the ninth planet is now recognized as a notable dwarf planet. Investigating its icy surface and elusive atmosphere prompts us to unveil the mysteries of this distant world. Exploring Pluto reveals that cosmic importance isn’t tied to its size.
Facts about Pluto:
- Pluto's surface is predominantly composed of a complex mixture of ices, including nitrogen, methane, and water ice. This intricate blend contributes to the planet's varied and distinct surface features.
- Pluto's orbit is highly eccentric, meaning it deviates significantly from a perfect circle. This unique orbital path takes Pluto closer to the Sun at times, and then swings it far away, distinguishing it from the more circular orbits of the eight classical planets.
- Pluto's tenuous atmosphere contains traces of methane, a volatile gas that plays a role in the planet's surface processes. Despite its thinness, the atmosphere influences the appearance and dynamics of Pluto's icy surface.

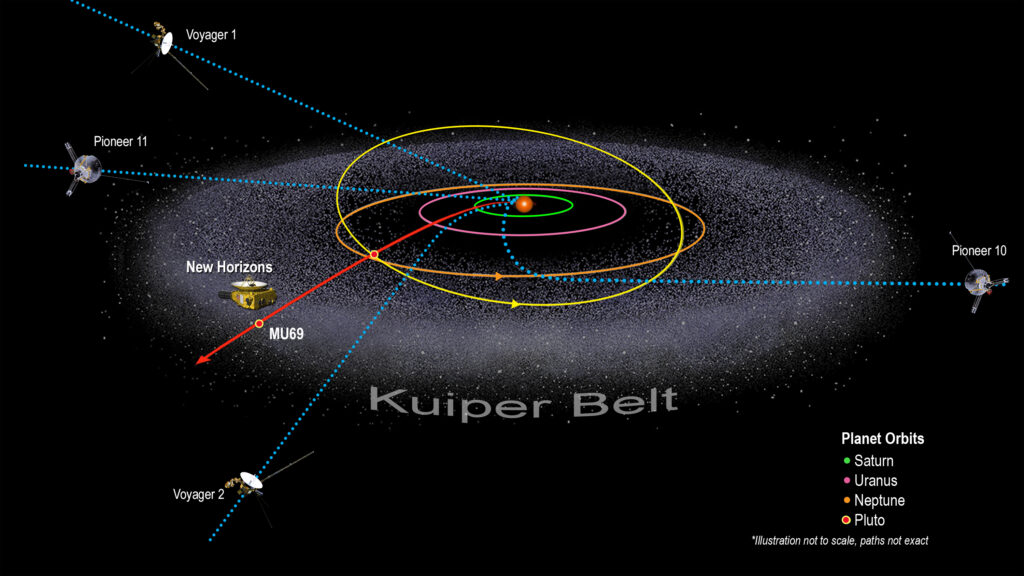
Kuiper Belt
Beyond Pluto, there’s a vast region in space known as the Kuiper Belt. It’s filled with icy objects and small planets. This cosmic neighborhood is situated far from Neptune. Within the Kuiper Belt, numerous remnants of celestial objects exist, each holding a unique story frozen within the icy confines of the Kuiper Belt.
Some notable residents of the Kuiper Belt, like Haumea and Makemake, challenge our understanding of the outer limits of our solar system. They possess distinct features and orbits that extend quite far, revealing the ever-changing nature of the Kuiper Belt within the broader concept of “what is in our solar system.”
Exploring this distant region helps us uncover the early history of our solar system. It serves as a kind of time capsule, preserving fragments that provide valuable insights into the origins and development of planets. As we journey through the Kuiper Belt, discovering the stories of these icy bodies and small planets, we continue to enhance our understanding of the vast expanse of our solar system.
Moons
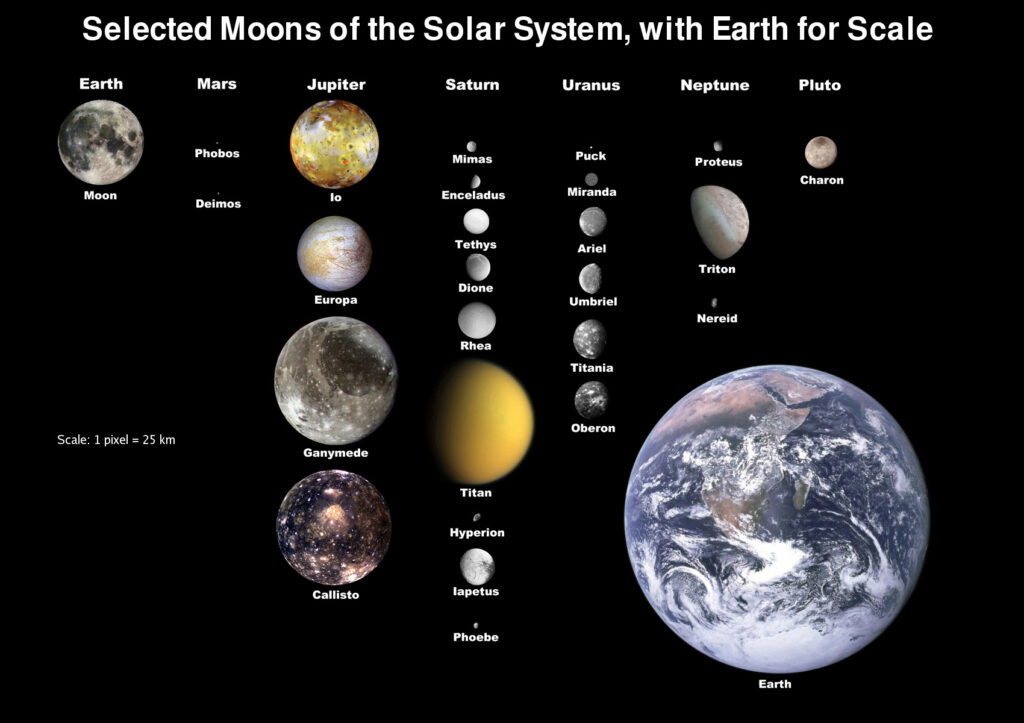
Moons, those captivating companions of planets, add a fascinating layer to the tapestry of our solar system. There are numerous moons orbiting various planets, each with its own unique characteristics and stories.
Jupiter, the largest planet, boasts a remarkable collection of moons, with the four largest known as the Galilean moons — Io, Europa, Ganymede, and Callisto. These moons, discovered by Galileo Galilei in 1610, showcase diverse landscapes, including volcanic activity on Io and the potential for subsurface oceans on Europa.
Saturn, famous for its stunning ring system, also hosts a captivating array of moons. Titan, the second-largest moon in the solar system, stands out with its thick atmosphere and methane lakes. Enceladus, another of Saturn’s moons, attracts attention for its geysers that spout icy particles into space.
Mars, our neighboring planet, has two small moons named Phobos and Deimos. These irregularly shaped moons are thought to be captured asteroids, adding a unique touch to Mars’ celestial company.
The Earth, our home, is accompanied by the Moon, Earth’s only natural satellite. The Moon has played a significant role in shaping our planet’s history and continues to be a subject of scientific exploration.
These are just a glimpse into the diverse world of moons in our solar system, each offering a unique perspective and contributing to the rich tapestry of celestial bodies that make up our cosmic neighborhood.
Beyond Our Solar System
Our journey now ventures beyond our solar system, exploring the vast cosmos around us. This leg of our exploration is a dive into the unknown, a quest to uncover mysteries beyond what is in our solar system.
Consider the intriguing realm of exoplanets—planets orbiting stars beyond our sun. The discovery of these distant worlds has broadened our understanding of the types of planets out there. Studying exoplanets provides insights into potentially habitable environments and expands our awareness of the vast possibilities beyond our immediate cosmic neighborhood.
Ongoing space missions, like the Voyager probes, act as ambassadors venturing into the interstellar depths. Their trajectory transcends the boundaries of our solar system, carrying messages and artifacts from humanity. These missions underscore our relentless curiosity about space.
Understanding the cosmos goes beyond scientific inquiry; it also sparks the human spirit, inspiring curiosity and contemplation about our place in the vastness of space. In this exploration of what is in our solar system, we acknowledge that the cosmic narrative extends far beyond the familiar orbits and celestial bodies we call home.
As we gaze into the cosmic abyss, we ponder profound questions that have captivated humanity for centuries. What lies beyond the stars we see in our night sky? Are there other civilizations, other stories waiting to be discovered in the cosmic expanse?
As our cosmic adventure ends, we stand at the crossroads of curiosity and discovery. What is in our solar system unfolds like a story, revealing the wonders that shape our cosmic neighborhood.
From the sun’s brilliance to the inner and outer planets’ stories, and the dynamic asteroid belt, each celestial body shares its tale. Dwarf planets, the Kuiper Belt, and moons challenge what we know about our solar system’s limits.
This cosmic quest is not just about science; it sparks our human spirit’s desire for knowledge and connection.

Andrew
With years of experience and a passion for exploring the cosmos, I want to be your go-to destination for all things celestial. My mission is to bring the wonders of the universe to your fingertips and demonstrate how the art of stargazing and telescope therapy can nurture not only your astronomical curiosity but also your mental health. Explore the cosmos with me and discover the profound connection between the night sky and your inner peace.








+ There are no comments
Add yours